The NVD Crisis: Gaps and Delays in Vulnerability Analysis
Since February 12th, 2024, the NVD has nearly halted its analysis of published Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs), resulting in a staggering 42% of CVEs lacking critical metadata such as severity (CVSS) scores and affected product information, with thousands of vulnerabilities receiving the status “AWAITING ANALYSIS”. As of March 11th, the NVD listing contains over 2,400 entries that have not been enriched. NIST hasn’t provided specific reasoning for this halt of analysis, hinting to process improvement enhancements, and referring to the creation of an unspecified “consortium”.
 A notification appearing on NVD listings for from February 12th onwards (source: NIST)
A notification appearing on NVD listings for from February 12th onwards (source: NIST)
This absence of timely analysis data poses significant risks to organizations that rely on NVD for vulnerability prioritization and remediation.
Without up-to-date severity scores and affected product details, organizations are left in the dark about the potential impact and urgency of newly discovered vulnerabilities. This lack of information hinders their ability to make informed decisions about patch management and risk mitigation strategies, ultimately increasing their attack surface and exposing them to potential breaches.
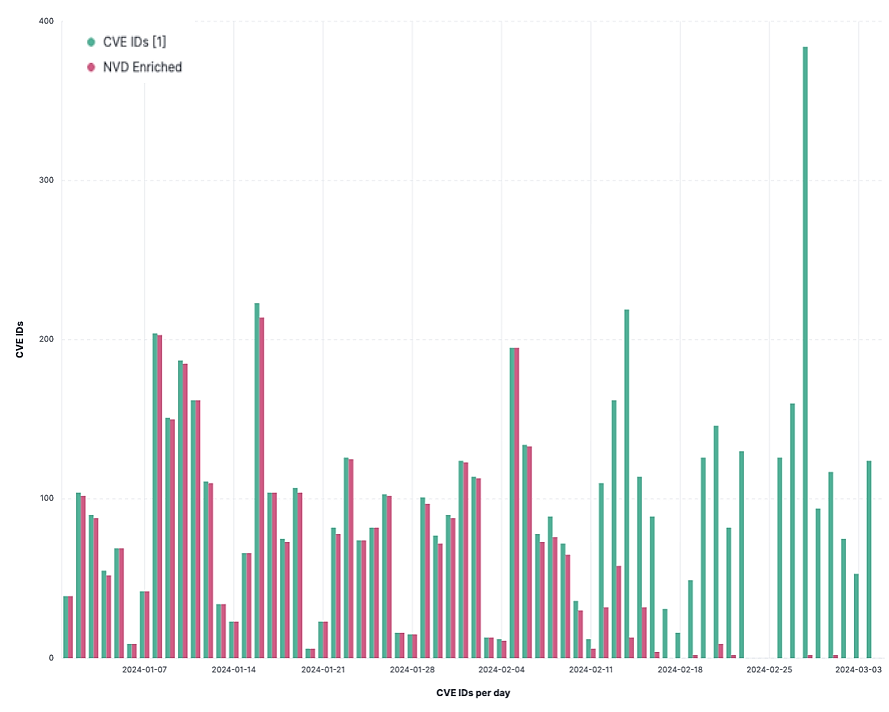 Comparison between # of published CVEs (green) and # of analyzed CVEs (red). Analysis has noticeably halted since mid-February (source: Anchore.com)
Comparison between # of published CVEs (green) and # of analyzed CVEs (red). Analysis has noticeably halted since mid-February (source: Anchore.com)
Morphisec’s Automated Moving Target Defense: Proactive Protection Against Unpatched Vulnerabilities
Morphisec’s Automated Moving Target Defense (AMTD) technology offers a powerful solution to bridge the gap created by the NVD’s delayed analysis. AMTD proactively prevents attacks on unpatched operating systems and application vulnerabilities by continuously morphing the attack surface, making it impossible for attackers to exploit known vulnerabilities.
Unlike traditional security solutions that rely on signature-based detection or behavioral analysis, AMTD operates at the memory level, randomizing and shifting the location of critical system components. This dynamic and unpredictable nature of AMTD renders attack vectors ineffective, as attackers cannot rely on static memory locations to execute their malicious code.
By providing immediate protection against unpatched vulnerabilities, AMTD allows organizations to maintain a strong security posture even in the absence of timely NVD analysis data. This proactive defense mechanism buys time for organizations to prioritize and address vulnerabilities based on their own risk assessments and business requirements, rather than being solely dependent on external vulnerability databases.
Virtual Patching: Extending Protection and Ensuring Compliance
In addition to AMTD, Morphisec’s virtual patching capabilities further enhance an organization’s ability to mitigate risks associated with unpatched vulnerabilities. Virtual patching acts as a compensating control, providing interim protection until official vendor patches are released and deployed.
Virtual patching is particularly crucial for end-of-life systems and applications that no longer receive vendor support or security updates. By implementing virtual patches, organizations can extend the life of these legacy systems without compromising their security posture or violating compliance requirements such as PCI DSS and HIPAA.
Morphisec’s virtual patching solution is lightweight and easy to deploy, with minimal impact on system performance. It enables organizations to adhere to their planned patching schedules without the need for emergency patching or business disruptions. This flexibility allows IT teams to allocate their resources more effectively and focus on strategic initiatives rather than constantly firefighting vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability Prioritization: Risk-driven Remediation Recommendations to Streamline Patching Efforts
In parallel to the compensatory controls and virtual patching provided by AMTD, Morphisec’s Vulnerability Prioritization helps to streamline patching efforts by providing risk-driven remediation recommendations tailored to business context, as well as enriching CVEs with EPSS scores (Exploit Prediction Scoring System) and CISA KEV (Known Exploited Vulnerability) listing information.
Application usage across organizations varies. Morphisec’s groups vulnerabilities according to business functions and assets (e.g. financial servers), hosts, applications, and maps actual usage. Together with the enrichment by EPSS and CISA KEV listing information, this enables security teams to prioritize patching efforts according to multiple strategies, according to the actual risk of the organization, saving costly resources, and achieving an effective reduction of the actual exposure to vulnerabilities.
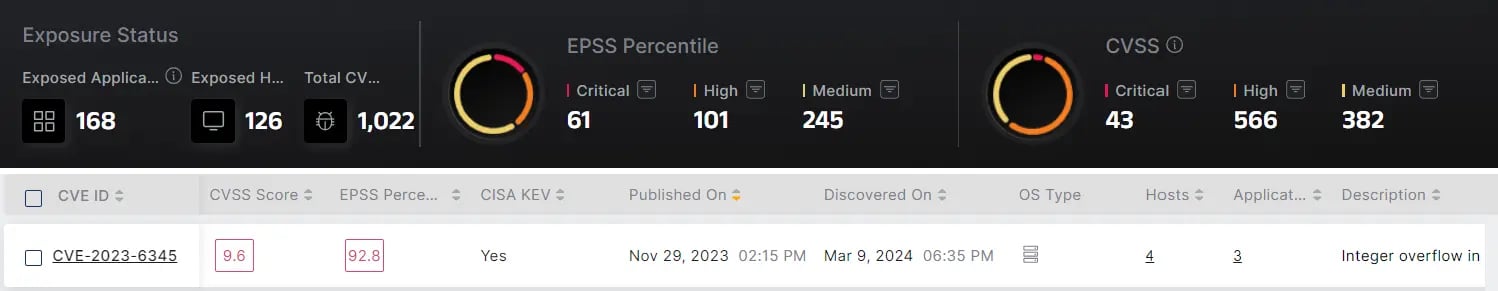
Enriched CVE listing showing EPSS Percentile, CISA KEV listing, number of impacted hosts and applications (Source: Morphisec.com)
Conclusion
The current gaps and delays in the National Vulnerability Database’s analysis data underscore the importance of proactive and adaptive vulnerability management. Morphisec’s Automated Moving Target Defense technology and virtual patching capabilities offer a comprehensive solution to address these challenges.
By leveraging AMTD’s proactive protection, organizations can defend against unpatched vulnerabilities and maintain a strong security posture even in the absence of timely NVD data. Virtual patching extends this protection to end-of-life systems and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
In an era where vulnerabilities are constantly evolving and the threat landscape is ever-expanding, Morphisec’s innovative solutions empower organizations to stay one step ahead of attackers. By adopting Morphisec’s Automated Moving Target Defense and virtual patching, organizations can proactively mitigate risks, ensure compliance, and maintain a robust security posture in the face of emerging threats.
https://blog.morphisec.com/national-vulnerability-database-defend-unpatched-vulnerabilities





